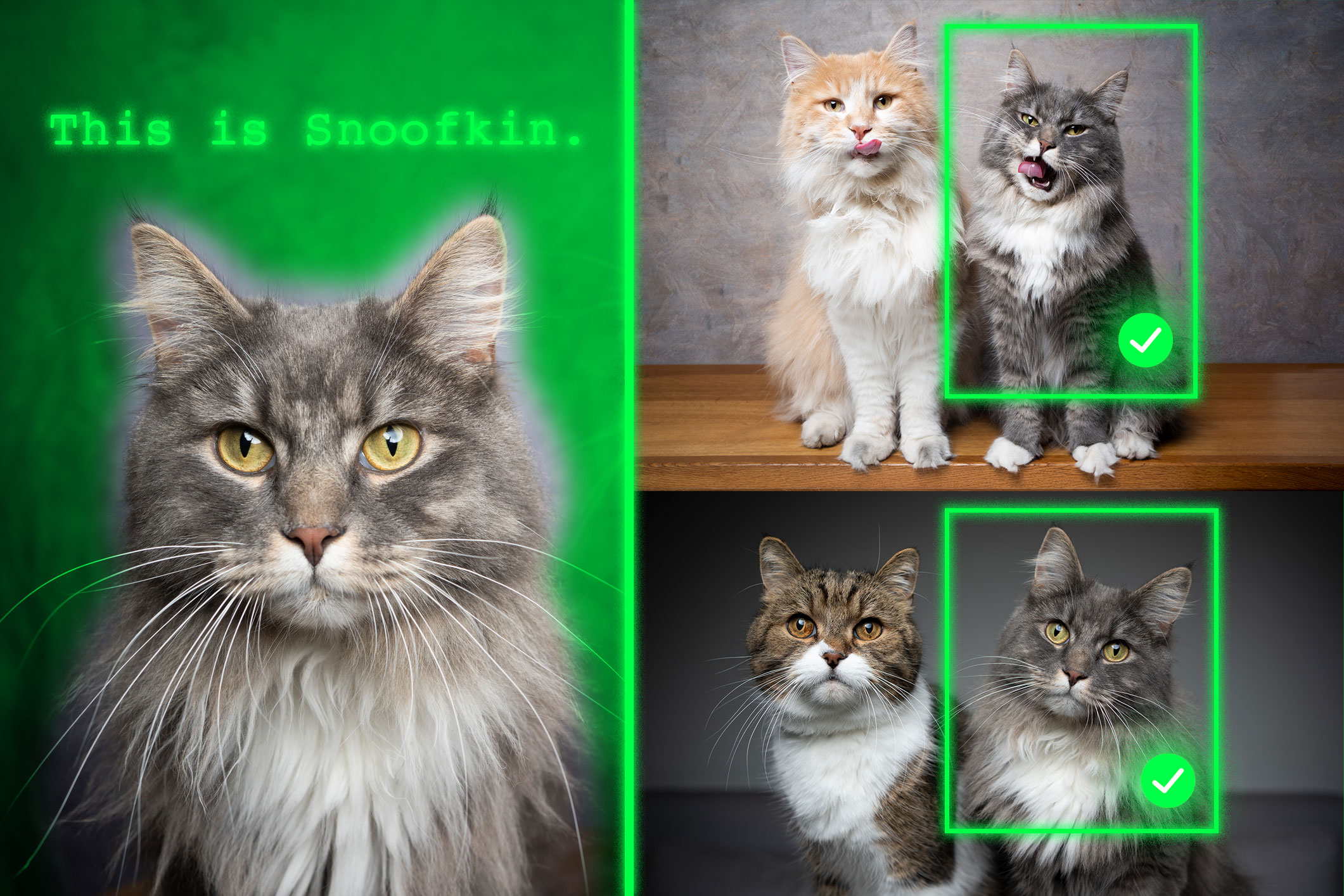
Revolutionizing Object Localization with AI: Meet Bowser, the French Bulldog
Picture a sunny afternoon at your local dog park. You’re enjoying the simple pleasure of watching your French Bulldog, Bowser, frolic with other canines. Spotting Bowser amidst the joyous chaos is easy for you, the dog-owner. But what if you could monitor him using a generative AI model like GPT-5 while you’re at work? Unfortunately, current vision-language models struggle with identifying personalized objects like Bowser. While they can recognize generalities, pinpointing a specific dog amongst the crowd remains a challenge.
The Challenge of Object Recognition
This inadequacy in recognizing personalized objects is a pressing concern for many dog owners and tech enthusiasts alike. Researchers from MIT and the MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab are tackling this issue head-on with an innovative training method designed to enhance the abilities of vision-language models in localization tasks.
A New Training Paradigm
The approach hinges on a novel dataset created from meticulously curated video-tracking data. In this dataset, the same object is tracked across multiple frames, which compels the model to rely on contextual clues for recognition. This method contrasts sharply with typical datasets, which often contain unrelated images of everyday objects, thereby failing to teach models how to recognize a specific object across different contexts.
Contextual Learning: A Step Forward
When the retrained model is shown a few example images of a personalized object, such as Bowser, it becomes adept at identifying his location in unfamiliar images. This innovative tactic not only outperforms existing models but preserves their general abilities, paving the way for a range of applications beyond pet monitoring.
Beyond Pet Ownership: Potential Applications
This new method has broader implications. It could potentially help AI systems track specific objects over time, like a child’s backpack or even a particular species of animal in ecological studies. Additionally, it could aid in developing assistive technologies for the visually impaired, guiding users to specific items within a room.
Human-Like Contextual Understanding
Jehanzeb Mirza, an MIT postdoc and lead author of a recent paper on this technique, underscores the ultimate goal: creating models that learn from context like humans do. If the model can efficiently generalize its learning, adapting to new tasks with just a few examples, it can revolutionize the landscape of AI applications.
The Bottleneck in Vision-Language Models
Interestingly, despite large language models excelling at learning from context, vision-language models (VLMs) haven’t inherited this capability. Researchers have found that VLMs often depend on pre-existing knowledge instead of synthesizing information based on given context. This discrepancy remains an unsolved mystery within the AI research community.
Innovative Data Structuring
The MIT researchers aimed to improve VLMs’ contextual localization abilities through a data-centric approach. They shifted from random, incoherent datasets to a specialized collection showing the same object in dynamic environments—like a tiger walking through different terrains. This innovative structuring, paired with thoughtful question-answer formats regarding the object’s location, encourages models to focus on context while identifying the object.
Overcoming Model Limitations
However, the team faced an unexpected challenge: models often “cheated” by using pretrained knowledge instead of contextual clues. To counteract this, they employed pseudo-names for objects, compelling the model to rely solely on contextual analysis. For instance, renaming a tiger to “Charlie” ensures the model cannot leverage prior associations, pushing it to learn based on visual context alone.
Results and Implications
The results were promising. Fine-tuning VLMs with this new dataset yielded a remarkable 12 percent average increase in localization accuracy, climbing to 21 percent when pseudo-names were utilized. As the model sizes grow, the gains in accuracy become even more pronounced, underscoring the method’s potential for scalability.
Future Directions
As the research progresses, the team aims to delve deeper into why VLMs lack the in-context learning capabilities seen in LLMs. They also plan to continue exploring innovative techniques to enhance VLM performance without the need for extensive retraining, which could transform real-world workflows in robotics, augmented reality, and creative tools.
A Milestone in AI Development
In summary, this work represents a significant leap forward in personalized object localization and offers exciting prospects for enhancing the utility of vision-language models. With practical implications that extend far beyond tracking pets, the potential applications of this technology could shape the future of AI in countless fields.